After you create a project, you can configure it in the ArcGIS QuickCapture designer using either the graphical interface or a JSON editor. You can configure the following:
- Project settings
- Groups
- Buttons
The following can be edited in the graphical interface for the project:
- General—Set the required or recommended location accuracy, distance threshold, display preferences, location editing preference, and quality of captured photos.
- Layers—Manage layers used by the project. By setting a layer as default, any new buttons added to the project will use fields of that layer. For all layers used in the project, you can also set default values and variables for all fields within each layer.
- Map—Select a map to be used by your project. By default, the organization default basemap will be used. Optionally, choose a different online basemap, web map, mobile map package, tile package, or vector tile package. Choose to show the map side by side with the buttons when the project is viewed on a tablet device in landscape orientation. Only maps with the Web Mercator spatial reference are supported.
- Project details—Edit the project thumbnail (use landscape images with a 3:2 aspect ratio), title, data recovery email, summary, description, and terms of use. Hyperlinks can be used in the project description.
- Exclusivity groups—Prevent multiple line, polygon, or streaming point buttons from capturing data at the same time by placing them in a group. Only one button in a group can be active at any one time.
- Project user input—Create project user inputs. These allow users to define values that will be captured along with captured records. An example is the cost center of the user.
- Webhooks—Configure webhooks used in the project and specify the name, target feature layer, webhook URL, and information to be included in the payload. You can add multiple webhooks in a project and set the status to be on or off for each of them.
The following can be edited in the graphical interface for groups:
- Label—Label shown in the project for the group.
- Number of columns—Number of columns in the group.
- Make group collapsable—Display preference of the group. If set to collapsable, the default state is expanded.
- Colors—Outline color of the group as an HTML hexadecimal value.
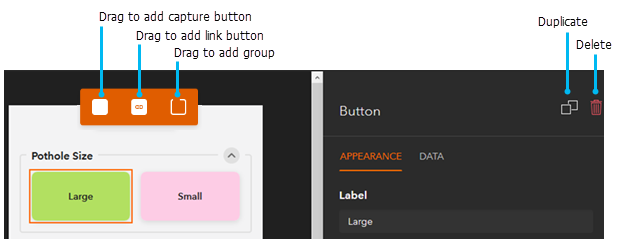
You can create groups by dragging the group icon onto the project preview.
You can use buttons to either capture data or launch a URL. The following can be edited in the graphical interface for buttons:
- Appearance—Configure the appearance of buttons in the project.
- Label—Button label and text size of small (default), medium, and large.
- Size—Button size. Use the slider to choose from smallest to largest.
- Shape—Button shape can be rectangle or rounded corner rectangle.
- Colors—Colors of the button background and outline as HTML hexadecimal values.
- Image—Button image. Consider the size of your button when choosing an image. Button images are limited to 1 MB.
- Data—Type of data to be collected for each field when the button is tapped.
- Target feature layer—The feature layer where captured data of the button is sent.
- Capture mode (points only)—Capture a single point or capture streaming points.
- Take photo—Off, optional, or required. Hide the camera preview. Use photo location for captured record.
- Capture fields—These can be fixed values, device variables (for example, speed or accuracy), or button user input variables that allow users to enter or select a value from a list once the button is pressed.
- Link—A dedicated URL to be launched when the button is pressed.
- Launch URL—A manually configured URL. This can be a website URL that begins with HTTPS or an app link that launches another app.
- Launch Survey123 field app—Construct the link to launch the ArcGIS Survey123 field app. Select a survey and predefine the input value of supported survey questions with fixed values, device variables, or a project user input variable. Optionally, choose to return to QuickCapture after submitting the survey.
You can create buttons that capture data by dragging the button icon on the project preview. The new button has the fields of the default layer. If a default layer has not been set for the project, the author must add the data source for the button by selecting it on the Data tab of the button side panel.
To add buttons that launch a URL, drag the link icon on the project preview. On the Link tab, choose URL to manually define the URL or choose Survey123 field app to select a survey to link to.
You can duplicate or delete an existing button. Select the button in the project preview and choose the Duplicate or Delete button on the Appearance tab of the button side panel.
You can edit these properties and more by changing the project JSON. You can copy and paste code between the QuickCapture designer and your preferred JSON editor or edit it directly in the designer. There is limited syntax checking in the designer, so be careful when making edits. Checking code snippets in an online JSON validator may be useful.
When editing properties of type decimal in the project JSON, you must always use a period (.) as the decimal separator. Other decimal separators will not work.
The following sections provide more detail about some of the most common customizations made to projects.
Streaming points
A project author can configure a point button to capture continuously, similar to how line and polygon buttons operate. Streaming point capture is useful when you want to record GNSS metadata and other data such as speed for every vertex along a path. Each vertex of the path is represented by a point and can be continuously automatically sent to ArcGIS.
If a button user input is applied to a point button, streaming mode cannot be enabled on that button. If streaming mode has already been selected for a point button, a button user input cannot applied to that button.
Streaming point capture is not designed to actively track the location of mobile workers. To learn more about types of point capture, see ArcGIS Tracker.
Fixed values
You can apply fixed values to fields when a button is pressed. This fixed text is defined by the author and constrained by the field type and length. For example, an integer field can not accept a decimal or text value.
Device variables
Device variables are used to automatically populate QuickCapture fields with common GIS attributes. Not all variables can be applied to all types of fields. For example, the timestamp variable only applies to fields of type date.
Some variables are automatically assigned to button fields that have a specific name. You may choose to manually create these named fields in your feature layer, or optionally, select Capture GPS receiver information when creating a feature layer in ArcGIS Online or creating a feature layer in ArcGIS Enterprise.
The following table lists variables that you can use with line and polygon layers:
| Variable | Description | Compatible field type | Name of field variable will be automatically assigned to |
|---|---|---|---|
| username | Currently signed-in user name. | Text | - |
| appVersion | Version of the QuickCapture mobile app. | String | - |
| operatingSystem | Platform and operating system verison. | String | - |
| positionSourceType | Category of the position source. Potential results are Unknown (0), User (1), System Location (2), External Device (3), and Network Device (4). | Integer | - |
| startTime | Date and time the button is activated. | Date | - |
| endTime | Date and time the button is deactivated. | Date | - |
| lengthM | Geodetic length in meters. | Double | - |
| lengthKM | Geodetic length in kilometers. | Double | - |
| lengthMI | Geodetic length in miles. | Double | - |
| areaM2 | Area in square meters, for polygon layers only. | Double | - |
| areaKM2 | Area in square kilometers, for polygon layers only. | Double | - |
| areaMI2 | Area in square miles, for polygon layers only. | Double | - |
The following tables list variables that you can use with point layers.
Device
| Variable | Description | Compatible field type | Name of field variable will be automatically assigned to |
|---|---|---|---|
| username | Currently signed-in user name. | Text | - |
| appVersion | Version of QuickCapture. | String | - |
| operatingSystem | Platform and operating system verison. | String | - |
| magneticDeclination | Angle between magnetic and true north in decimal degrees. | Double | - |
| azimuth | Compass bearing of device when the record was captured, where true north is 0, east is 90, south is 180, and west is 270. | Double | esrisnsr_azimuth |
| pitch | Pitch of device when the record was captured, where 0 represents the device face up and 90 represents the device tilted upright, perpendicular to the ground. | Double | - |
| roll | Roll of device when the record was captured, where 0 represents the device face up, 90 represents the device rolled to the right, -90 represents the device rolled to the left, and 180 represents the device face down. | Double | - |
Note:
When a point is manually edited, the magneticDeclination, azimuth, pitch, and roll variables are cleared.
Location
| Variable | Description | Compatible field type | Name of field variable will be automatically assigned to |
|---|---|---|---|
| positionSourceType | Category of the position source. Potential results are Unknown (0), User (1), System Location (2), External Device (3), and Network Device (4). | Integer | esrignss_positionsourcetype |
| sensorName | Location sensor name. This is the same variable used for internal position source or external device. It replaces pluginName used in older releases. | Text | esrignss_receiver |
| captureTime | Time of capture in UTC. | Date | esrignss_fixdatetime |
| latitude | Latitude in decimal degrees. | Double | esrignss_latitude |
| longitude | Longitude in decimal degrees. | Double | esrignss_longitude |
| altitude | Altitude above sea level or ellipsoid in meters. | Double | esrignss_altitude |
| horizontalAccuracy | Horizontal accuracy of the x,y coordinates in meters. | Double | esrignss_h_rms |
| verticalAccuracy | Vertical accuracy of the z-coordinate in meters. | Double | esrignss_v_rms |
| DMS | Location as a space-separated string in degrees minutes and seconds. | Text | - |
| DDM | Location as a space-separated string in degrees and decimal minutes. | Text | - |
| USNG | Location in U.S. National Grid. | Text | - |
| MGRS | Location in Military Grid Reference System. | Text | - |
Note:
When a point is manually edited, sensorName, altitude, horizontalAccuracy, and verticalAccuracy variables are cleared.
Travel
| Variable | Description | Compatible field type | Name of field variable will be automatically assigned to |
|---|---|---|---|
| speedMS | Ground speed in meters per second. | Double | - |
| speedKPH | Ground speed in kilometers per hour. | Double | esrignss_speed |
| speedMPH | Ground speed in miles per hour. | Double | - |
| speedKTS | Ground speed in knots. | Double | - |
| verticalSpeedMS | Vertical speed in meters per second. | Double | - |
| verticalSpeedMPH | Vertical speed in miles per hour. | Double | - |
| verticalSpeedKPH | Vertical speed in kilometers per hour. | Double | - |
| verticalSpeedKTS | Vertical speed in knots. | Double | - |
| direction | Direction of travel measured clockwise from north in decimal degrees. | Double | - |
| directionCardinal4 | Direction of travel generalized as one of the four cardinal directions. Potential results are N, E, S, and W. | Text | - |
| directionCardinal8 | Direction of travel generalized as one of the eight cardinal directions. Potential results are N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W and NW. | Text | - |
Note:
When a point is manually edited, speedMS, speedKPH, speedMPH, speedKTS, verticalSpeedMS, verticalSpeedMPH, verticalSpeedKPH, verticalSpeedKTS, direction, directionCardinal4, and directionCardinal8 variables are cleared.
Photo
| Variable | Description | Compatible field type | Name of field variable will be automatically assigned to |
|---|---|---|---|
| camHeading | Compass bearing of the device's rear camera when the photo was captured, where true north is 0, east is 90, south is 180, and west is 270. Also saved to the photo EXIF tag GPSImgDirection. Be aware that camHeading is not reliable when images are captured with camRoll values greater than ±10 degrees. | Double | - |
| camPitch | Pitch of the device's rear camera when the photo was captured, where 0 represents the camera looking down toward the ground, and 90 represents the device looking forward perpendicular to the ground. | Double | - |
| camRoll | Roll of the device's rear camera when the photo was captured, where 0 represents no roll, 90 represents the device rolled to the right, and -90 represents the camera rolled to the left. Roll beyond ±45 degrees will result in the device orientation being switched from portrait to landscape, and camHeading, camPitch and camRoll angles will be adjusted accordingly. | Double | - |
| hfov | Horizontal field of view for the camera lens measured in degrees. Calculated from photo EXIF tag FocalLength35mmFilm. Returns null if EXIF tag is missing. | Double | - |
| vfov | Vertical field of view for the camera lens measured in degrees. Calculated from photo EXIF tag FocalLength35mmFilm. Returns null if EXIF tag is missing. | Double | - |
| photoLatitude | Latitude when the photo was captured, in decimal degrees. Also saved to the photo EXIF tag GPSLatitude. | Double | - |
| photoLongitude | Longitude when the photo was captured, in decimal degrees. Also saved to the photo EXIF tag GPSLongitude. | Double | - |
External GNSS
| Variable | Description | Compatible field type | Name of field variable will be automatically assigned to |
|---|---|---|---|
| fixType | Type of position fix for the coordinate. Potential results are NoFix (0), GPS (1), DifferentialGPS (2),PrecisePositioningService (3), RTKFixed (4), RTKFloat (5), Estimated (6), Manual (7), Simulator (8), and SBAS (9). | Integer | esrignss_fixtype |
| deviceAddress | Address of the device. | Text | - |
| sensorName | Name of the device. This is the same variable used for internal position source or external device. It replaces deviceName used in older releases. | Text | esrignss_receiver |
| deviceType | Type of external device. Potential results are Unknown (-1), Bluetooth (0), Serial Port (1), and Bluetooth LE (2). | Integer | - |
| networkName | Name of the network position source. This is only available for network location providers. | Text | - |
| networkAddress | Address of the network position source. This is only available for network location providers. | Text | - |
| networkPort | Port of the network position source. This is only available for network location providers. | Integer | - |
| geoidSeparationCustom | Difference between the WGS-84 earth ellipsoid and mean sea level as defined by the user in the app settings. This is available for all location provider types. | Double | - |
| antennaHeight | Distance from the antenna to the ground surface is subtracted from altitude values in meters. | Double | - |
| altitudeType | Selected altitude type. Potential results are altitude above mean sea level (0) and height above ellipsoid (1). | Integer | - |
| geoidSeparation | Difference between the WGS-84 earth ellipsoid and mean sea level as reported by the GNSS receiver in meters. This is also sometimes referred to as orthometric height. | Double | - |
| accuracyType | Type of accuracy reported by the horizontalAccuracyand verticalAccuracy properties. Potential results are RMS (0) and DOP (1). RMS is root mean square accuracy. This is calculated based on a 68 percent confidence interval for latitude, longitude, and altitude errors reported in the GST sentence provided by the receiver. If the receiver does not support GST, DOP is used instead. DOP is a dilution of precision based accuracy. This uses a constant user-estimated range error (UERE) value to estimate horizontal and vertical accuracies. | Integer | - |
| confidenceLevelType | Accuracy confidence level. Potential results are 68 percent (0) and 95 percent (1). | Integer | - |
| positionAccuracy | Mean radial spherical error in meters. This encompasses both horizontal and vertical error. | Double | - |
| latitudeError | Value of latitude 1-sigma error in meters. This property is only populated if your positioning device supports GST sentences in NMEA streams. | Double | - |
| longitudeError | Value of longitude 1-sigma error in meters. This property is only populated if your positioning device supports GST sentences in NMEA streams. | Double | - |
| altitudeError | Value of altitude 1-sigma error in meters. This property is only populated if your positioning device supports GST sentences in NMEA streams. | Double | - |
| hdop | Positional data's Horizontal Dilution of Precision (HDOP). | Double | esrignss_hdop |
| vdop | Positional data's Vertical Dilution of Precision (VDOP). | Double | esrignss_vdop |
| pdop | Positional data's Positional Dilution of Precision (PDOP). The equation used to determine PDOP is PDOP^2 = HDOP^2 + VDOP^2. | Double | esrignss_pdop |
| differentialAge | Age of the differential signal and correction used by the GPS receiver to differentially correct the position in seconds. | Double | esrignss_correctionage |
| referenceStationId | Differential reference station ID (DSID) of the station used by the GPS receiver. | Integer | esrignss_stationid |
| satellitesVisible | Number of positioning satellites visible at the time of location capture. | Integer | - |
| satellitesInUse | Number of positioning satellites being used to return the position data. | Integer | esrignss_numsats |
Note:
When a point is manually edited, all external GNSS variables are cleared.
Exclusivity groups
An exclusivity group is used to ensure only one button within the group is active at any time. Consider capturing a series of lines that represent the changing condition of a footpath. As you travel along the path, the condition may be excellent, good, or poor. Tap the excellent button to start capturing a line representing an excellent section of footpath. When the condition changes, tap the poor button immediately. Capture of the excellent line stops, and capture of the poor line starts.
Exclusivity groups are typically applied to polyline and polygon buttons, but you can also add point buttons that are streaming mode enabled. You can include buttons from different template groups in a single exclusivity group, and you can apply multiple exclusivity groups to a project.
Project user input variable
The project user input variable value is populated by the app user, and you can apply it to one or more buttons in a project. The app user enters the value; however, the project author must define the buttons and fields to which the variable will apply.
A project user input variable is different from a button user input variable in the following ways:
- Only one project user input variable is defined per project.
- Its value is entered by the user before pressing a button. If the user input is set as required, the user is prompted to enter this value when starting the project but can edit the value at any time.
- You can apply its value to any text fields in any buttons.
- It is defined by the project author in Settings > Project user input.
- You cannot apply it to a text field that is configured with a range domain or coded value domain.
Properties of the project user input variable are as follows:
- Label—Text that will appear as the title of the project user input page in the app.
- Input type—Can be single-line text, multiline text, or choice list. You can add, delete, and reorder choices. Optionally, you can allow free text entry with choice lists.
- Apply hint—Display hint text on the project user input dialog box in the app.
- Apply an input mask—Define the format for data entry by using characters and symbols to define an input mask.
- Required—Specifies whether the mobile app user must provide the user input value before they can press any button. When not required, the user can optionally enter a user input value by selecting the edit button (next to the user input value displayed at the top of the screen) and typing a value.
Note:
When applying a user input value to a feature layer with required fields, ensure that its required property is set to true to avoid submission errors.
To assign a project user input variable to a capture field of a button, on the Data tab, from the drop-down menu of the capture field, select Project user input. You can apply project user input variables only to text fields without domains.
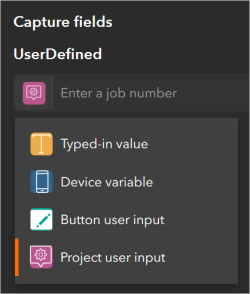
In the mobile app, the user is prevented from entering text that exceeds the length of the data field.
Button user input variable
A button user input variable value is populated by the app user after a button is pressed in a project. The app user enters the value; however, the project author must define the buttons and fields to which button variables will apply.
A button user input variable is different from a project user input variable in the following ways:
- Many button user input variables can exist in one project.
- Values are entered by the user after pressing a button.
- Can be applied to only one field within the one button.
- Configured by the project author on the Data tab for each button.
Properties of the button user input variable are as follows:
- Label—Text that will appear as the title of the project user input dialog box in the app.
- Text field type—Can be single-line text or multiline text.
- Apply hint—Display hint text on the project user input dialog box in the app. This is not applicable when configured with a range or coded value domain.
- Apply an input mask—Define the format for data entry using characters and symbols to define an input mask.
- Required—Specifies whether the mobile app user must provide the user input value after a button is pressed.
Note:
When applying a user input to a feature layer with required fields, ensure that its required property is set to true to avoid submission errors.
Depending on field type, different user input variable parameters are available:
- String—User input label, display as multiline or single line, hint, input mask, required.
- Integer—User input label, required.
- Double—User input label, required.
To assign a button user input variable to a capture field of a button, on the Data tab, from the drop-down menu of the capture field, select Button user input and select Create new.
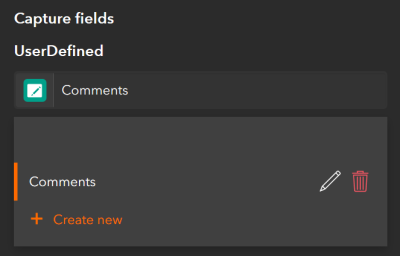
If you create a button user input for a field that has a domain (either coded value or range), the choices are presented to the user as a single choice list. Free text cannot be entered when a coded value domain is present. When a range domain is present, data entry is limited by the range.
Input masks
An input mask defines the format for data entry using characters and symbols as part of a project or button user input variable. When you apply an input mask to a user input variable, values entered by the user must follow the specific pattern defined by the input mask.
To apply an input mask to your user input variable, define the mask in the userInputs.domain.inputMask property.
The following table lists the characters and symbols that you can use in an input mask:
| Character | Meaning |
|---|---|
A | ASCII alphabetic character required. Characters can be A through Z and a through z. |
a | ASCII alphabetic character permitted but not required. |
N | ASCII alphanumeric character required. Characters can be A through Z, a through z, and 0 through 9. |
9 | ASCII digit required. Digits can be 0 through 9. |
D | ASCII digit required. Digits can be 1 through 9. |
H | Hexadecimal character required. Characters can be A through F, a through f, and 0 through 9. |
B | Binary character required. Characters can be 0 through 1. |
> | All following alphabetic characters are uppercase. |
< | All following alphabetic characters are lowercase. |
! | Switch off case conversion. |
\ | Escape the special characters listed above to use them as separators. |
The mask consists of a string of characters and separators, optionally followed by a semicolon and the character used for blanks. The blank characters are always removed from the text after editing. The following table lists example masks:
| Example mask | Description |
|---|---|
>A<xxxxxxxxxxxx | Text that starts with a capital letter followed by any lowercase characters. |
AAA-AAA-AAA;_ | Unique identifier that uses dashes as separators and underscores to represent each character that is to be completed. |
B9.99;- | Represents a pH value. The number is constrained to start only with 0 or 1 and can only include two decimal places. A dash is used to represent each character that is to be completed. |
999-99-9999 | United States Social Security number. |
(999) 999-9999 | United States phone number. |
900 kg | Weight in kilograms between 0 and 999. |
99999 | United States 5-digit ZIP Code. |
AAA | IATA airport code. |
Webhooks
Webhooks are a widely supported method used to allow multiple applications to interact with each other, using HTTP POST requests to pass callbacks between them. For more information, see Wikipedia's page on webhooks. Common uses for webhooks include sending notifications via email or SMS, posting messages to social media, automatically writing records to a spreadsheet, and updating enterprise databases.
In QuickCapture, webhooks can be set up and activated when a record is submitted. For example, after a successful submission of information to the feature layer, the webhook could be called and trigger another action, such as sending a notification email, appending the record to a spreadsheet, and sending an alert.
Your workplace may have its own webhook provider, but a wide variety of third-party workflow services are available, such as Integromat, Microsoft Power Automate, Zapier, and tray.io. You can use all of these to incorporate QuickCapture as a trigger for a greater automated process. In particular, Integromat has a QuickCapture module, allowing you to integrate QuickCapture into your webhook workflow with minimum difficulty, and without the need to configure the webhook in the QuickCapture designer or to input a payload URL.
There are many ways you can use QuickCapture as a trigger in your workflows. To get started, Integromat has templates that you can use to include attachments in your email notifications, add records to spreadsheets, and create calendar items. To learn more, see Automate workflows with Integromat.
You can configure a webhook in the QuickCapture designer by choosing Webhooks from the project Settings. When creating a new webhook, provide the following parameters:
- Name—The name of the webhook (unique within the project).
- Target feature layer—Select a single feature layer. The payload is sent to the configured webhook URL each time a record is submitted to this layer.
- Webhook URL—Where the project information is sent. An external webhook provider must provide this.
- Event data—Choose what information is included in the payload, including project details, information of the user, portal and submitted record, and response from the server.
- Status—Determines whether this webhook is enabled when the project is saved.
Project validation
Analysis is performed to help validate data and diagnose your project configuration when you open, save, or share the project. Guidance is provided to help fix errors or warnings on the Messages pane. Click the error or warning message to locate the issue.
You can save the project with warnings. However, you cannot save it until all the errors are resolved. Issues that may prevent saving include the following:
- Invalid data sources—Feature layers and map that have been deleted or unshared.
- Empty required fields—Fields marked as required must have a device variable, user input, or fixed value defined. When assigning a user input to a required field, ensure the user input variable is also marked as required.
- Invalid project settings—Incompatible values for recommended and required horizontal accuracy, settings marked as required must have valid input, invalid webhook configuration, or a project without any buttons configured.
Oriented imagery (BETA)
You can configure QuickCapture to automatically capture photo metadata that enables the use of Oriented Imagery in ArcGIS. Enabling a QuickCapture project with oriented imagery allows you to better manage and visualize your non-oblique imagery. Enabling oriented imagery on a project does not result in a change in the mobile user experience but does provide users with the following capabilities.
- Select a location or asset and see which photos cover it.
- Select a photo and see its footprint.
- See a correlation between ground features (on the map) and image features.
To enable oriented imagery in designer, you need a QuickCapture project that is configured to take photos. Follow these steps to enable oriented imagery.
- Go to Settings > Layers.
- Select the menu for the point feature layer that the photos will be submitted to, and click Enable oriented imagery.
QuickCapture adds fields to the selected feature layer and automatically map device variables to these fields in your project. These fields store metadata such as horizontal and vertical field of view, camera heading, pitch, and roll.
Enabling oriented imagery also creates an oriented imagery catalog (OIC) item that contains information including a reference to the configured point feature layer and a range of settings and default values. It is this item that clients such as custom web apps and ArcGIS Pro consume to work with the oriented imagery.
- For each button in your project that captures a photo, ensure Use photo location for captured records is enabled.
- Click Save.
When oriented imagery is enabled, the mobile app calculates the camera heading, roll, and pitch at the time of capturing each photo.
To visualize and exploit the photos with the Oriented Imagery sample app, use either of the following options in the QuickCapture designer.
- Click View on the confirmation dialog box after enabling oriented imagery on the layer.
- Go to Settings > Layers, open the menu for the layer and click View oriented imagery.