ArcGIS GeoPlanner dashboards display key performance indicator (KPI) and baseline indicator information in gauges, numeric values, and charts so you can quickly visualize and understand the impacts of design decisions in real time. You can access the dashboard widget from many segments of the GeoPlanner workflow. The dashboard displays qualitative and quantitative information about your design layer or data layer point, line, and polygon features. As you add, update, and delete features in your design layers, the dashboard automatically updates KPIs to provide you with immediate feedback on the impacts of your design decisions. Baseline indicators connected to data layers must be manually recalculated before their impact can be assessed with the dashboard.
The GeoPlanner dashboard allows you to track impacts across multiple indicators so you can easily assess advantages and disadvantages while trying to balance multiple competing priorities for your design outcome. These indicators can be represented as charts, numerical values, or gauges in the dashboard. Charts provide qualitative indicators of a plan's performance. Gauges and numerical values provide a quantitative indication of a plan's performance. Once a collection of charts, numerical values, and gauges have been defined for measuring the performance of designs in a planning project, their configuration can be easily shared with other project team members as a way to standardize the parameters used for evaluating alternatives among the team.
You can configure multiple charts, numerical values, and gauges within a dashboard so that you can monitor several different indicators. You can also modify KPIs with data layer features using baseline modifiers. You can share a dashboard with your project team members or the template from which a project is created. This helps standardize the indicators used within a project or across any project created from a specific template. Sharing a dashboard saves time by reducing configuration.
You can open the dashboard by clicking the Dashboard button  on the map toolbar.
on the map toolbar.
There are three types of dashboard items: charts, numerical values, and gauges.
Charts
Charts help you understand the distribution of feature types within a dataset and, optionally, can be configured to show a qualitative indication of suitability for your plans. Each dashboard chart in GeoPlanner displays two graphics: primary and secondary charts. The primary chart displays the distribution of unique feature types for the selected layer. The secondary chart displays a summary of features from an assessment layer or evaluation model that lies beneath those features highlighted in the primary chart.
The following graphic represents a dashboard chart that contains a primary chart of design layer land-use polygon features and a secondary chart of an assessment layer of neighborhood home values. The yellow pie wedge represents residential features in this plan. The secondary chart summarizes the types of neighborhood home value features within those residential features.
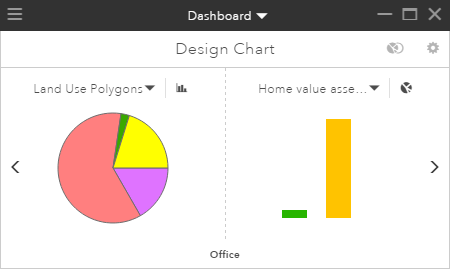
Primary charts can help answer questions such as the following:
- How many hectares of residential land are in my design?
- What is the total length of highways in my transportation plan?
- How many wells are within an area?
Secondary charts show how design layers overlay with an assessment or evaluation model layer. They can help answer questions such as the following:
- How much of my proposed residential land is within a five-minute walk to a park?
- How much of my proposed highway expansion is within an area of low population density?
- How many of my wells are located within a 100-year flood plain of a river or stream?
Charts are dynamic. They update each time you create, modify, or delete features in your design layers.
Assessment layers and evaluation models
Assessment or evaluation model layers help you understand the suitability of a development activity in an area. These layers increase your spatial awareness so you can plan and design more effectively in a given geographic context. They are used in the secondary charts to display a relationship to the features in the primary chart.
Assessment layers are created using one of the following methods:
- Run an analysis tool from the Analysis drop-down in the Explore tab, and then reclassify the result layer using the classify function.
- Reclassify any feature layer using the classify function.
Evaluation models are the output from weighted raster overlay.
Numerical values
Numerical values allow you to analyze your features quantitatively. Numerical values on your dashboard are based on KPI and baseline indicator values. You can use these values to show raw counts of your data, averages, standard deviations, and more.
Numerical values can help you answer questions such as:
- What is the population within the boundaries of my design area?
- What is the average area of all land use layers in my scenario?
- What is the population density of rare butterflies in a habitat, normalized by the total population of rare butterflies in my data set?
Gauges
Gauges help you understand the effect or outcome of your designs relative to a specific, calculated performance metric. Gauges allow you to define ranges and targets appropriate to specific indicators you want to evaluate your plans against. With KPIs, the value presented on the gauge is calculated in real time using an equation consisting of feature type filters, feature attribute values, constants, and arithmetic operators that you define specific to your KPIs. Gauges created with baseline indicators must be manually recalculated for their results to show.
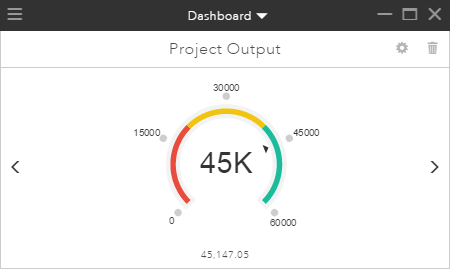
Gauges help you answer questions such as the following:
- What is the projected population of a housing development?
- What is the projected yield of a crop within an area?
- How many jobs could be created from a new commercial development?
Study areas
Study areas represent planning sub—areas. Study areas help you focus on a specific location like a neighborhood or a watershed. When you activate a study area, the dashboard computes metrics for scenario features within or that intersect that study area.
Non-design layers
You can set non–design layers in the primary chart of the dashboard. These layers must be polygon feature layers with a unique value renderer. Dashboard charts configured with non-design layers in the primary chart only report on visible features.
Maximize the dashboard modal
The GeoPlanner Dashboard modal allows you to view a single chart or gauge item at a time, or you can view the entire dashboard simultaneously:
- Maximize button— Increases the size of the modal to the maximum allowed by your screen resolution so that you can view the values of many or all of your dashboard items at once.
- Restore button—Returns the modal to its default size where a single dashboard item is displayed.
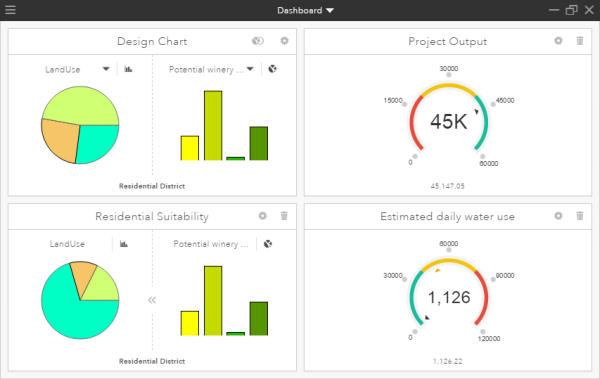
Note:
When maximizing the dashboard, you can hide other interface elements so that all charts and gauges can be easily seen without obstruction.
Display selected features
You can display dashboard metrics against selected features in scenario layers. This helps you focus your metrics on subsets of features. Use the following process to compute metrics against selected features:
- In GeoPlanner, display the dashboard by clicking on the Dashboard button
 on the map.
on the map. - Click Design > Select Feature > Multi-Select
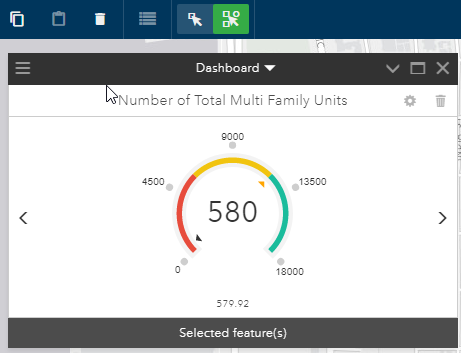
- In the Multi-select dialog box, click the Layer drop-down arrow and choose the scenario design layer from which you want to select features.
- Click New set and Draw Rectangle.
- On the map, draw a rectangle around the features you want to select.
Dashboard settings
You can specify how features are included in dashboard items in the Dashboard Settings window. Click the Dashboard Options button  to access the Dashboard Settings window.
to access the Dashboard Settings window.
- On the Dashboard modal, click the Dashboard Options button
 .
. - Click Dashboard Settings.
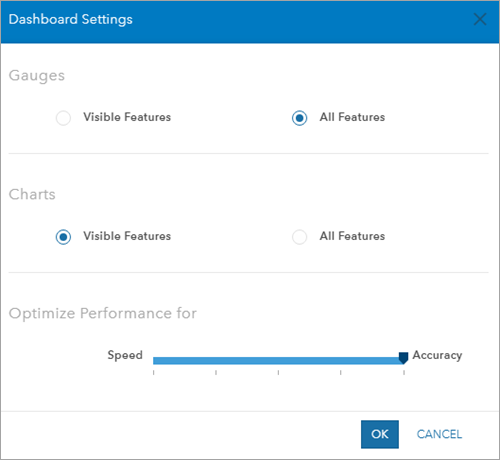
The Dashboard Settings window appears.
- In the Gauges section, choose how gauges show data on your dashboard:
- Visible Features: Gauges on the dashboard will only load if the features they represent are visible on the map. Choosing this option can make your project more performant.
- All Features: Gauges on the dashboard load for all features in the scenario.
- In the Charts section, choose how charts show data on your dashboard:
- Visible Features: Charts on the dashboard will only load if the features they represent are visible on the map. Choosing this option can make your project more performant.
- All Features: Charts on the dashboard load for all features in the scenario.
- In the Optimize Performance for section, adjust the slider between the two values shown below to change your project's performance.
Note:
This slider controls how a feature is generalized when fetched from your ArcGIS organization and included in a dashboard calculation. Generalization is the process of simplifying features for change of scale or resolution. The slider represents a maximum offset tolerance. Vertices within that tolerance are removed such that the features displayed in the map contain a subset of the original feature vertices.
When the slider is set to Accurate, no generalization occurs. Area, perimeter and length calculations in charts and gauges are accurate. As you move the slider toward Speed, your features are more generalized. This reduces the accuracy of area, perimeter and length calculations in charts and gauges.
Consider moving the Optimize Performance slider to greater generalization tolerances when working at regional, national, or global scales.